When you need AWS managed Active directory for Windows instances in an autoscaling group, use the following steps to update launch configuration with instance AMI. These steps are required to ensure newly added instances in autoscaling group are connected to the active directory.
Prerequisites
- Active directory service provided by AWS should be created
- Either the EC2 instance launched in same VPC of Active directory or there is VPC peering
- Active directory user login should be created
- Autoscaling group should be created
To automatically join a newly added Windows instance in an autoscaling group to AWS Managed Microsoft AD directory:
Select the instance you are going to take AMI and first, manually join that instance to active directory using this steps.
Login to the instance as administrator user and now we need to create a task in task scheduler. This task will change the hostname of server and join the instance to active directory at system startup
Save the following powershell script as add-host.ps1 under C drive. Don’t forget to replace the your_AD_user_password, your_AD_username, and AD_domain_name in the script with the corresponding details.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# Get IP Address of host
$myIpAddress = "{0:x}" -f (Get-WmiObject Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration | ? { $_.IPAddress -ne $null}).ipaddress
# split ip into 4 octets, prep to convert to hexadecimal
$octets = $myIpAddress.split(".")
foreach ($octet in $octets) {
$hexOctet = [System.String]::Format("{0:X}",[System.Convert]::ToUInt32($octet))
# Prepend 0 to beginning if less than 2 digits
if ( $hexOctet.Length -lt 2 ) {
$hexOctet = "0" + "$hexOctet"
}
$hostName = "$hostName" + "$hexOctet"
}
$hostName = $hostName
$password = "your_AD_user_password" | ConvertTo-SecureString -asPlainText -Force
$username = "your_AD_username"
$newname=hostname
$credential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential($username,$password)
$instanceID = invoke-restmethod -uri http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/instance-id
Add-Computer -DomainName AD_domain_name -NewName $hostname -Credential $credential -Force -Restart
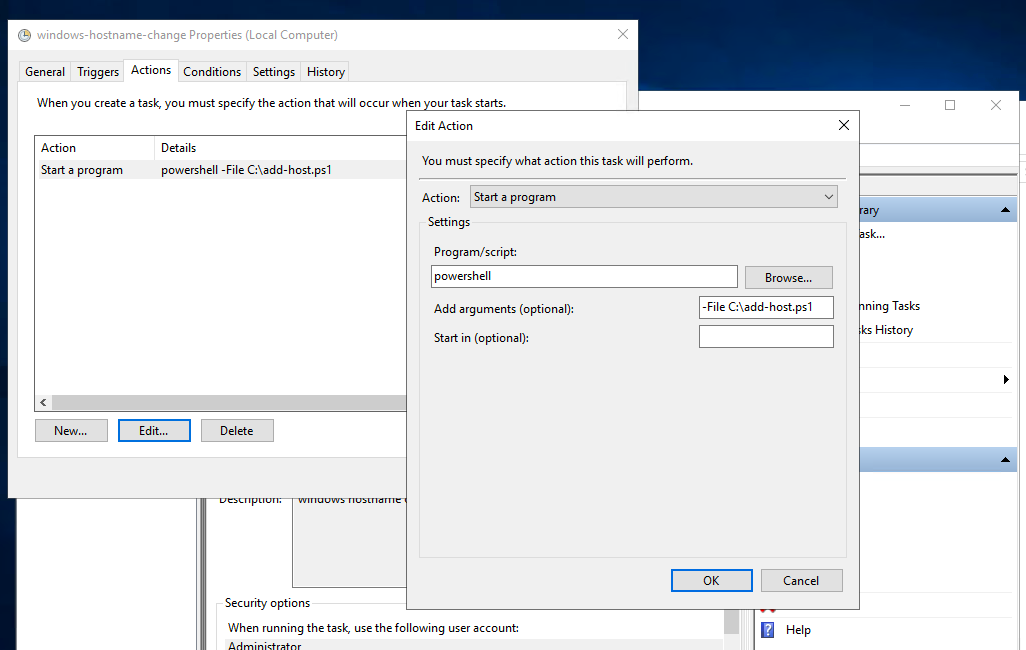
Open Task Scheduler and create task with following details:
- The trigger will be At startup and action will be Start a program and then select program as powershell. Enter the following as argument:
1
-File C:\add-host.ps1
Take a AMI of the server ( Select No reboot and Name properly to identify )
Launch an instance with the AMI on same subnet.
RDP the instance using Active directory user.
Change the Preferred DNS server and Alternate DNS server addresses to the IP addresses of the AWS Directory Service-provided DNS servers.
Disable hostchange task scheduler job by right-clicking on the task.
Change hostname of the server and change the Member of settings from active directory domain to workgroup. You can enter it as WORKGROUP. Instance will be restarted.
Login to the instance again as Local Administrator user.
Ensure the DNS entry persent on the ipv4 settings are IP addresses of the AWS Directory Service-provided DNS server.
Enable Task scheduler job
Add Local Administrator user to task scheduler job. You need to enter the local administrator password for this.
Take the final AMI and update the autoscaling group launch configuration with the latest AMI ID.
Increase the instance count in autoscaling group and test if the newly launched instance is joined in active directory or not.
That’s it!